Last night I finished reading ‘Neroism is in the Air’ – Germany: 1890-1914, being chapter 6 of ‘The Proud Tower’, Barbara W. Tuchman’s excellent analysis of the build up to WWI.
Writing of music, philosophy, theatre and literature, the author focusses on the country’s competitive culture. She begins with the strident strains of Richard Strauss reflecting Nietzsche’s concept of ‘rule by the best’ and the Kaiser’s arrogant military ambitions, continuing to Wilde’s Salome and other bloodthirsty tragedies which captured the soul of much of the nation, uncannily presaging the current conflicts in her own country. Gentler voices are drowned by the violence of others. Tuchman does not neglect the considerable contribution of Jewish people to all aspects of life, despite the rising anti-Semitism.
Today was one to stay inside and keep dry. I therefore scanned another batch of colour slides made in May 2008 and February 2009.











All black and white images in this post have been converted.
The body of Emmeline Pankhurst lies here. Her memorial has been bound with the suffragette colours.
‘Emmeline Goulden was born on 14 July 1858 in Manchester into a family with a tradition of radical politics. In 1879, she married Richard Pankhurst, a lawyer and supporter of the women’s suffrage movement. He was the author of the Married Women’s Property Acts of 1870 and 1882, which allowed women to keep earnings or property acquired before and after marriage. His death in 1898 was a great shock to Emmeline.
In 1889, Emmeline founded the Women’s Franchise League, which fought to allow married women to vote in local elections. In October 1903, she helped found the more militant Women’s Social and Political Union (WSPU) – an organisation that gained much notoriety for its activities and whose members were the first to be christened ‘suffragettes’. Emmeline’s daughters Christabel and Sylvia were both active in the cause. British politicians, press and public were astonished by the demonstrations, window smashing, arson and hunger strikes of the suffragettes. In 1913, WSPU member Emily Davison was killed when she threw herself under the king’s horse at the Derby as a protest at the government’s continued failure to grant women the right to vote.
Like many suffragettes, Emmeline was arrested on numerous occasions over the next few years and went on hunger strike herself, resulting in violent force-feeding. In 1913, in response to the wave of hunger strikes, the government passed what became known as the ‘Cat and Mouse’ Act. Hunger striking prisoners were released until they grew strong again, and then re-arrested.
This period of militancy was ended abruptly on the outbreak of war in 1914, when Emmeline turned her energies to supporting the war effort. In 1918, the Representation of the People Act gave voting rights to women over 30. Emmeline died on 14 June 1928, shortly after women were granted equal voting rights with men (at 21).’ (BBC.co.uk)
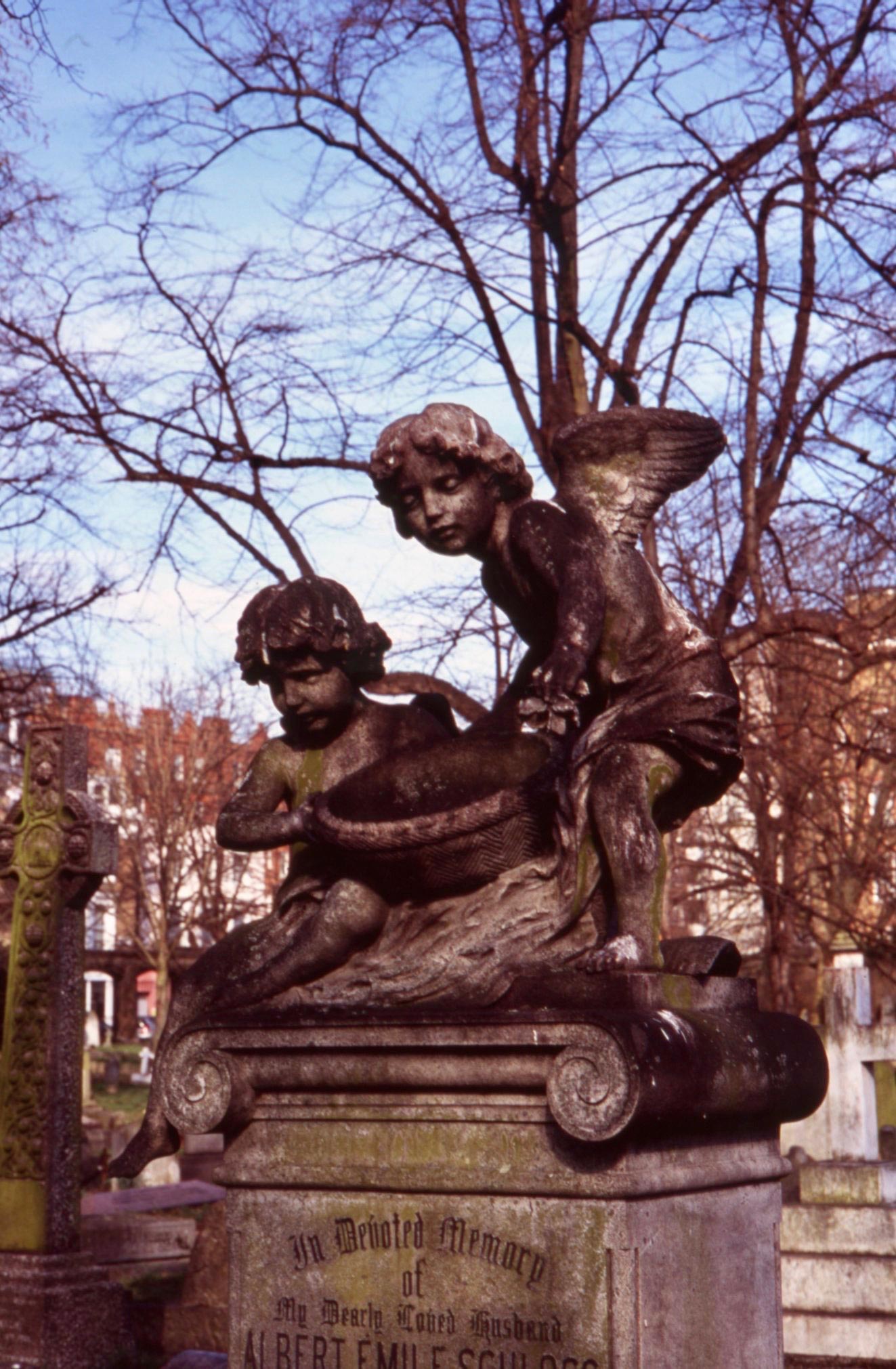
‘Little is known about Albert Emile Schloss (1847-1905), except that he was from Mayance, the French name for the city of Mainz on the Rhine in Germany. According to the cemetery’s burial register, Albert died at the Hyde Park Hotel in London.’ (royal parks.org.uk). These two cherubs adorn his plinth.
Metropolitan Anthony Bloom is commemorated with his mother, Xenia.
‘His Eminence Metropolitan Anthony Bloom (June 6, 1914 – August 4, 2003) was bishop of the Diocese of Sourozh, the Russian Orthodox Church in Great Britain and Ireland.
He was born in Lausanne, Switzerland. He spent his early childhood in Russia and Persia, his father being a member of the Russian Imperial Diplomatic Corps. His mother was the sister of Alexander Scriabin, the composer. During the Bolshevik Revolution the family had to leave Persia, and in 1923 they settled in Paris where the future metropolitan was educated, graduating in physics, chemistry and biology, and taking his doctorate in medicine, at the University of Paris.
In 1939, before leaving for the front as a surgeon in the French army, he secretly professed monastic vows in the Russian Orthodox Church. He was tonsured and received the name of Anthony in 1943. During the occupation of France by the Germans he worked as a doctor and took part in the French Resistance After the war he continued practising as a physician until 1948, when he was ordained to the priesthood and sent to England to serve as Orthodox Chaplain of the Fellowship of St. Alban and St. Sergius. He was appointed vicar of the Russian patriarchal parish in London in 1950, consecrated as Bishop in 1957 and Archbishop in 1962, in charge of the Russian Orthodox Church in Great Britain and Ireland (the Diocese of Sourozh). In 1963 he was appointed Exarch of the Moscow Patriarchate in Western Europe, and in 1966 was raised to the rank of Metropolitan. At his own request he was released in 1974 from the function of Exarch, in order to devote himself more fully to the pastoral needs of the growing flock of his diocese and all who come to him seeking advice and help.
Metropolitan Anthony received honorary doctorates from Aberdeen University (“for preaching the Word of God and renewing the spiritual life of this country”); from the Moscow Theological Academy and Seminary for his theological, pastoral, and preaching work; from Cambridge University; and from the Kiev Theological Academy. His first books on prayer and the spiritual life (Living Prayer, Meditations on a Theme, and God and Man) were published in England, and his texts are now widely published in Russia, both as books and in periodicals.
Many Orthodox Christians in Great Britain and throughout the world consider Metropolitan Anthony to be a saint.’ (https://orthodoxwiki.org/Anthony_(Bloom)_of_Sourozh)
‘Allan and Iris Burnside were the grandchildren of the founder of Eaton’s, once Canada’s largest chain of department stores until financial difficulties in the 1970s led to their eventual takeover by Sears Canada in 1997, and closure in 2002. Iris Burnside died aboard the Lusitania when the ship was torpedoed by a German U-boat on 7 May 1915. Her mother, Josephine, was also aboard but survived. Allan died in Paris in 1937. The memorial is believed to have been erected on Josephine’s death in 1943.’ (https://historicengland.org.uk/listing/the-list/list-entry/1403346)
This evening we dined on Jackie’s cottage pie with carrots al dente, tender runner beans and thick, meaty, gravy with which she drank Hoegaarden and I drank Mendoza Malbec 2019.



